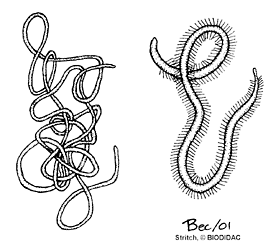
Nematomorpha
Horsehair worms


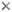
This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxReferences
Bresciani, J. 1991. Nematomorpha. Pages 197–218 in: Microscopic Anatomy of Invertebrates. F. W. Harrison and E. E. Ruppert, eds. Wiley-Liss, New York.
Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. 1996. Zur Morphologie, Biologie und Phylogenie der Nematomorpha. Cuvillier-Verlag, Göttingen.
Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. 1996. The nervous system of Nectonema munidae and Gordius aquaticus, with implications for the ground pattern of the Nematomorpha. Zoomorphology 116:133-142.
Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. 1997. Nematomorpha. Süßwasserfauna von Mitteleuropa Vol. 4/4. J. Schwoerbel and P. Zwick (eds.) Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart, Germany, 124 pp.
Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. 1998. Phylogenetic relationships of the Nematomorpha — a discussion of current hypothesis. Zoologischer Anzeiger 236:203–216.
Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. 2001. Horsehair worms (Nematomorpha) as parasites of praying mantids with a discussion of their life cycle. Zoologischer Anzeiger 240(2):167-179.
Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. 2002. Are the genera of Nematomorpha monophyletic taxa? Zoologica Scripta 31:185-200.
About This Page
Page copyright © 2002
All Rights Reserved.
Citing this page:
Tree of Life Web Project. 2002. Nematomorpha. Horsehair worms. Version 01 January 2002 (temporary). http://tolweb.org/Nematomorpha/2473/2002.01.01 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/



 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site