Sporormiaceae
Asa Kruys- Chaetopreussia
- Pleophragmia
- Preussia
- Pycnidiophora
- Sporormia
- Sporormiella
- Spororminula
- Westerdykella
Introduction
Sporormiaceae includes ca. 100 species divided into eight genera, of which Sporormiella is the most species-rich (Barr 2000). Members of Sporormiaceae are widespread and are most commonly found on various types of animal dung, but they also occur on soil, wood, plant debris, decaying textiles and exceptionally human tissue. Ascospores of Sporormiaceae can be found in ancient soil samples and sediments and are thus, useful tools in paleoecological studies (Hausmann et al. 2002, van Geel et al. 2002, Burney et al. 2003).
Characteristics
Sporormiaceae is a group of fissitunicate ascomycetes characterized by perithecioid or cleistothecioid ascomata and asci with a narrow endotunica and a scarcely developed apical apparatus (Barr 2000). The characteristic ascospores are thick-walled and dark brown, strongly constricted at septa and often fragmenting into part-spores at maturity. Another typical feature of the spores in many species is the distinct germ slits.




1. Ascus of Sporormia fimetaria. © 2006 Asa Kruys. 2. Ascus of Sporormiella sp. © 2006 Asa Kruys. 3. Ascospore of Sporormiella sp. with germslits. © 2006 Andrew Miller
Discussion of Phylogenetic Relationships
Sporormiaceae forms a monophyletic group, but the circumscription of several genera within the family is unclear and they are in need of revision. Especially the limits separating Preussia from Sporormiella are unclear, and some authors consider them to be separated and others do not (Guarro et al. 1997, Bell 2005). The circumscription of genera in Sporormiaceae has been based on a comparatively small number of easily observed ecological and morphological characters, like ascoma type, substrate choice, and presence or absence of germ slits in the ascospores (von Arx & van der Aa 1987, Barr 2000). These characters are, however, poor predictors of phylogenetic relationships (Arenal et al. 2005, Nyberg Kruys 2005).
References
Abdullah, S. K., A. H. Al-Saadoon, and J. Guarro. 1999. New and interesting coprophilous ascomycetes from Iraq. Nova Hedwigia 69: 201-216.
Ahmed, S. I., and R. F. Cain. 1972. Revision of the genera Sporormia and Sporormiella. Canadian Journal of Botany 50: 419-477.
Arenal, F., G. Platas, and F. Pelaez. 2004. Variability of spore length in some species of the genus Preussia (Sporormiella). Mycotaxon 89: 137-151.
Arenal, F., G. Platas, and F. Pelaez. 2005. Two new Preussia species defined based on morphological and molecular evidence. Fungal Diversity 20: 1-15.
Arx von, J. A., and H. A. van der Aa. 1987. Spororminula tenerifae gen. et sp. nov. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 89: 117-120.
Barr, M. E. 2000. Notes on coprophilous bitunicate Ascomycetes. Mycotaxon 76:105- 112.
Bell, A. 2005. An illustrated guide to the coprophilous Ascomycetes of Australia. CBS Biodiversity Series, vol. 3. CBS, Utrecht.
Burney, D. A., G. S. Robinson, and L. P. Burney. 2003. Sporormiella and the late Holocene extinctions in Madagascar. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 100: 10800-10805.
Cain, R. F. 1934. Studies of coprophilous Sphaeriales in Ontario. Univ. of Toronto Studies 38, Toronto.
Cain, R. F. 1961. Studies of coprophilous ascomycetes. VII. Preussia. Canadian Journal of Botany 39: 1633-1666.
Cejp, K., and A. A. Milko. 1964. Genera of the Eurotiaceae with 32 ascospores ľ I. Westerdykella. Ceska Mykologie 18: 82-84.
Clum, F. M. 1955. A new genus in the Aspergillaceae. Mycologia 47: 899-901.
Dissing, H. 1992. Notes on the coprophilous pyrenomycete Sporormia fimetaria. Persoonia 14: 389-394.
Doveri, F. 2004. Fungi Fimicoli Italici: A guide to the recognition of basidiomycetes and ascomycetes living on faecal material. Associazione Micologica Bresadola, Trento.
Guarro, J., S. K. Abdullah, J. Gene, and A. H. Al-Saadoon. 1997. A new species of Preussia from submerged plant debris. Mycological Research 101: 305-308.
Guarro, J., A. H. Al-Saadon, and S. K. Abdullah. 1997. Two new coprophilous species of Preussia (Ascomycota) from Iraq. Nova Hedwigia 64: 177-183.
Khan, R. S., and R. F. Cain. 1979. The genera Sporormiella and Sporormia in East Africa. Canadian Journal of Botany 57: 1174-1186.
Locquin-Linard, M. 1977. ┴ propos des genres non ostiolÚs placÚs dans la famille des Microascaceae. Revue de Mycologie 41: 509-523.
Lorenzo, L. E. 1994. A new hairy species of Sporormiella. Mycological Research 98: 10-12.
Nyberg Kruys, ┼. 2005. Phylogenetic relationships and species richness of coprophilous ascomycetes. Doctoral thesis, Umeň University.
Stolk, A. C. 1955. Emericellopsis minima sp.nov. and Westerdykella ornata gen.nov., sp.nov. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 38: 419-424.
Valldosera, M., and J. Guarro. 1990. Estudios sobre hongos coprˇfilos aislados en Espa˝a XV. El gÚnero Preussia (Sporormiella). Boletin de la Sociedad Micologica de Madrid 14: 81-94
Title Illustrations

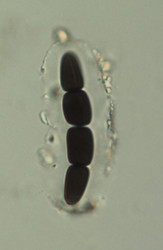
| Scientific Name | Sporormiella sp. |
|---|---|
| Comments | Squash mount of a Sporormiella fruitbody |
| Specimen Condition | Dead Specimen |
| Identified By | ┼. Kruys |
| Copyright |
© 2006

|
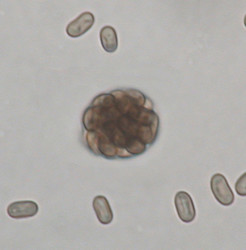
| Scientific Name | Sporormiella sp. |
|---|---|
| Specimen Condition | Dead Specimen |
| Identified By | ┼. Kruys |
| Body Part | Ascospore |
| Copyright |
© 2006

|
About This Page
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to Asa Kruys at
Page copyright © 2007
All Rights Reserved.
- First online 19 March 2007
- Content changed 19 March 2007
Citing this page:
Kruys, Asa. 2007. Sporormiaceae. Version 19 March 2007 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Sporormiaceae/60141/2007.03.19 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/










 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site