Pseudocaeciliidae
Emilie Bess and Kevin P. Johnson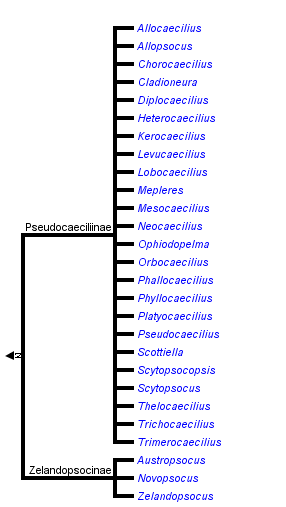

This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxIntroduction
The family Pseudocaeciliidae contains about 300 species in 23 genera distributed worldwide, with highest diversity in Asia. Two species are known from North America in the genus: Pseudocaecilius citricola from Florida and Texas, and P. tahitiensis from Florida and several regions of Mexico.
These are medium-sized bark lice (2-3 mm, nymphs up to 3 mm) with robust bodies. Body colors are brown or yellow. Pseudocaeciliids inhabit leaves and can often be found in clusters of dead leaves on tree branches. Some species live under sparse webbing, alone or in small groups.
Characteristics
Synapomorphies
None.
General Characters
- Head: Antennae have 13 segments.
- Legs: Tarsi have 2 or 3 segments.
- Abdomen: Abdomen has 2 or 3 vesicles (inflatable sacs) on underside.
- Wings:
- Wings are usually membranous; forewing occasionally coriaceous (“leathery”) but with distinct venation.
- Forewing veins with "Caecillius" pattern:
- Areola postica relatively narrow and long, free of vein M.
- Veins Rs and M are joined by a crossvein or fused for part of their length.
- Forewings appear hairy or fuzzy:
- Hairs on margin of forewing form crossing pairs.
- Forewing veins have more than one row of hairs.
- Hindwing:
- Hindwing veins Rs, M, Cu are fused at base.
- Hairs on margin are abundant and form crossing pairs on the hind margin.
- Hairs on veins are in single row.
- Male:
- Phallosome has complex sclerotization on tip.
- Hypandrium is ornamented with rugose areas and a transverse marginal comb.
- Female:
- Subgenital plate is bilobed.
- Gonapophyses are complete and well developed:
- Dorsal valve is pointed and have a large preapical lobe, sometimes closely associated with subgenital plate.
- Ventral valve is pointed and have a large preapical lobe.
- External valve is very large and hairy.
How to Know the Family
- Medium-sized bark lice (2-3 mm in length).
- Body colors are brown or yellow.
- Abdomen has 2 or 3 vesicles (inflatable sacs) on underside.
- Forewing areola postica is relatively narrow and long.
- Hairs on margin of forewing form crossing pairs.
- Hindwing veins Rs, M, Cu are fused at base.
- Hairs on margin are abundant and form crossing pairs on the hind margin.
- Hairs on hindwing veins are in a single row.
Family Monophyly
Pseudocaeciliidae is likely not monophyletic, according to both morphological and molecular data. There are no morphological characters supporting monophyly in the family (Yoshizawa 2002). Molecular analysis of including 11 species of the family indicates that the family is not monophyletic and shows ambiguous relationships with families Calopsocidae and Philotarsidae (18S nDNA; Johnson et al. 2004).
References
Johnson, K. P. & E. L. Mockford. 2003. Molecular Systematics of Psocomorpha (Psocoptera). Systematic Entomology 28: 409-40
Johnson, K. P., K. Yoshizawa, and V. S. Smith. 2004. Multiple origins of parasitism in lice. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B 271:1771-1776.
Lienhard, C. and C. N Smithers. 2002. Psocoptera (Insecta) World Catalogue and Bibliography. Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle, Geneva, Switzerland.
Mockford, E. L. 1993. North American Psocoptera (Insecta). Gainesville, Florida: Sandhill Crane Press,
New, T.R. 2005. Psocids, Psocoptera (Booklice and barklice), 2nd edition: Handbooks for the Identification of British Insects. Vol. 1, Part 7. Royal Entomological Society, London, UK.
Smithers, C. N. 1996. Psocoptera. Pp. 1-80, 363-372 (Index) in Wells A. (ed.) Zoological Catalogue of Australia. Vol. 26. Psocoptera, Phthiraptera, Thysanoptera. Melbourne: CSIRO Publishing, Australia.
Yoshizawa, K. 2002. Phylogeny and higher classification of suborder Psocomorpha (Insecta: Psocodea:'Psocoptera'). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 136: 371-400.
Title Illustrations

| Scientific Name | Heterocaecilius solocipennis |
|---|---|
| Location | Japan |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Identified By | K. Yoshizawa |
| Life Cycle Stage | adult |
| View | lateral |
| Size | 3mm |
| Copyright | © 2006 Kazunori Yoshizawa |
About This Page
Emilie Bess

Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign, Illinois, USA
Kevin P. Johnson

Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign, Illinois, USA
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to Emilie Bess at and Kevin P. Johnson at
Page copyright © 2009 Emilie Bess and Kevin P. Johnson
All Rights Reserved.
- First online 25 March 2009
- Content changed 25 March 2009
Citing this page:
Bess, Emilie and Kevin P. Johnson. 2009. Pseudocaeciliidae. Version 25 March 2009 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Pseudocaeciliidae/14475/2009.03.25 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/






 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site