Euphasmida
Stick & Leaf Insects
Erich Tilgner

This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxIntroduction
Euphasmida are commonly referred to as stick and leaf insects. Exquisitely camouflaged, many species look like twigs and may have the appearance of being covered by lichens, mold, bird feces, or moss. The leaf-like forms usually bear a striking resemblance to foliage, exhibiting leaf veins, mildew spots and even apparent insect feeding damage.
Their primary means of avoiding predators is crypsis. If discovered, they either play dead (catalepsy), or they try to scare the predator with a startle display which can include wing flashing, leg kicking, or spastic motion. Some species also release an irritating "tear gas-like" spray when disturbed (see Eisner et al. 1997). In addition, many Euphasmida can purposely lose some of their legs to help free them from a predator's grasp. If this occurs during the immature stages, they can regenerate the lost limbs during successive molts.
Compared to other insects, Euphasmida are large, and a few are gigantic. Several species measure over 200 mm in length (Brock 1999), and the worlds' largest extant terrestrial arthropod is the Euphasmida Phobaeticus serratipes, with one documented female measuring 555 mm (Seow-Choen 1995). Since Euphasmida are wonderful looking insects, relatively easy to rear in captivity, they are popular as pets and for displays at zoological gardens (Seiler et al. 2000).
Characteristics
Their tarsi possess five articles unlike Timema which have three. The cerci are simple being composed of one article. With the exception of the enigmatic genus Agathemera, Euphasmida possess some elongation of the body segments, and the mesothorax is usually elongated.
Euphasmida are hypothesized to be a monophyletic group because of several unique anatomical features they exhibit (Tilgner et al., 1999). For example:
- They have a cusp instead of a grinding lobe on the mandible
- Internally, the prothorax has rudimentary sternal projections for muscle attachment.
Discussion of Phylogenetic Relationships
Bradler (2000) hypothesized that the endemic South American genus Agathemera is the sister group to the remainder of Euphasmida. This hypothesis was falsified by Tilgner (2002) who proposed that the subfamily Aschiphasmatinae represents a monophyletic sister group to the remainder of the order. Tilgner (2002) considers Agathemera as the most basal clade in the crown group of Euphasmida. Tilgner (2002) was not able to resolve the relationships of the crown group with much certainty. Whiting et al. (2003) presented a phylogeny of Euphasmida as part of their hypothesis about wing evolution, but Aschiphasmatinae were not included. Sven Bradler (pers. comm.) is in the process of extending the work done by Whiting et. al. and should propose a more robust phylogenetic hypothesis of Euphasmida crown group phylogeny soon.
The relationship of Electrobaculum gracilis and of the species of Pseudoperla to the other crown group Euphasmida is uncertain. These extinct species are similar to Agathemera in that their mesothorax is not elongated. Their abdominal musculature cannot be examined, however, making their placement ambiguous. The remaining extinct species have features indicating they belong to the clade with the remaining Euphasmida, but no obvious synapomorphies link them with any group of extant species.
Fossil Record
Tilgner (2000) has recently provided a review of the Phasmida fossil record, and concluded that they are not an ancient clade of Insecta. The oldest Euphasmida fossils date to 49-44 million years ago. They are from Grube Messel (Darmstadt, Germany) and Clarno Nut Beds (Oregon, USA). Oligocene and Miocene fossils are known from Florissant shale (Colorado, USA), Baltic, and Dominican Republic amber.
Fossil euphasmid specimens. Left (top): A nymph of a Euphasmida in Dominican Republic amber. Right (bottom): A nymph of Pseudoperla lineata fossilized in Baltic amber. Photographs copyright © 2001, Erich Tilgner.
Euphasmida feed almost exclusively on the leaves of Angiosperms. Their phylogenetic and morphological diversification was probably due to an ability to exploit resources and new niches provided by these plants as they dominated terrestrial ecosystems during the later part of the Cretaceous Period and Cenozoic Era.
Note on Common Names
A stick insect is any Euphasmida that is tubular and has a greatly elongated body. Leaf insects are flattened and look like leaves. Many Euphasmida do not fit neatly into either the stick or leaf category, and it is best to refer to them simply as phasmids.
References
Bradler, S. 2000. On the systematic position of Agathemera Stål 1875 within the Phasmatodea (Insecta). Zool. Anal. Com. Sys. 103, Suppl. III (Abstr. 93.1):99.
Brock, P.D. 1999. The amazing world of stick and leaf-insects (R. Fry Ed.). Cravitz Printing Co., Essex, England.
Camousseight, A. 1995. Taxonomic review of the genus Agathemera (Phasmatodea: Pseudophasmatidae) in Chile. Rev. Chilena de Entomol. 22: 35-53.
Eisner, T., R.C. Morgan, A.B. Attygalle, S.R. Smedley, K.B. Herath, & J. Meinwald 1997. Defensive production of quinoline by a phasmid insect (Oreophoetes peruana). J. Exp. Biol. 200: 2493-2500.
Günther, K. 1953. Über die taxonomische Gliederung und die geographische Verbreitung der Insektenordnung der Phasmatodea. Beiträge zur Entomol. 3:541-563.
Seiler, C., S. Bradler, R. Koch 2000. Ratgeber Phasmiden; Pflege und Zucht von Gespenstschrecken, Stabschrecken und Wandelnden Blättern im Terrarium. Bede-Verlag 144pp.
Seow-Choen, F. 1995. The longest insect in the world. Malay Nat. 48:12.
Tilgner, E. H., Kiselyova, T. G., and McHugh, J. V. 1999. A morphological study of Timema cristinae Vickery with implications for the phylogenetics of Phasmida. Dtsche. Entomol. Z. 46(2):149-162.
Tilgner, E. 2001. Fossil Record of Phasmida (Insecta: Neoptera). Insect Syst. Evol. 31:473-480.
Tilgner, E. 2002. Systematics of Phasmida. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Georgia.
Whiting, M. F., S. Bradler, and T. Maxwell. Loss and recovery of wings in stick insects. Nature. 421 (2003): 264-267.
Information on the Internet
- Systematics of Phasmida. Full text of Erich Tilgner's Ph. D. Dissertation.
- Loss and recovery of wings in stick insects. Full text of Whiting et al. 2003.
- Sungaya-Phasmatodea
- Bugs in Cyberspace
- (ASPER) Association pour la Systématique des Phasmes et l'Etude de leur Répartition
- The Stick Insects (Phasmida) of South Africa. Compiled by P.D. Brock
- Guide to the stick and leaf insects of New Guinea. By Heinz van Herwaarden.
- Werkgroep PHASMA
- Biology of Phasmids
Title Illustrations

| Scientific Name | Phyllium bioculatum |
|---|---|
| Comments | a typical leaf insect |
| Image Use |
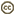 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
© 2001

|
| Scientific Name | Aplopus |
|---|---|
| Comments | undescribed species, mating pair, male is below female |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Sex | male and female |
| Image Use |
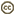 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
© 2001

|
| Scientific Name | Oxyartes spinosissimus |
|---|---|
| Comments | a stick insect that has the appearance of being covered by lichen |
| Specimen Condition | Live Specimen |
| Image Use |
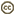 This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. This media file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0.
|
| Copyright |
© 2001

|
About This Page
The author thanks Katja-Sabine Schulz and David R. Maddison for converting this page into the correct format for the Tree of Life. Tatiana Kiselyova kindly provided a review of this work.

University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to Erich Tilgner at
Page copyright © 2001
 Page: Tree of Life
Euphasmida. Stick & Leaf Insects.
Authored by
Erich Tilgner.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Euphasmida. Stick & Leaf Insects.
Authored by
Erich Tilgner.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- First online 29 August 2001
- Content changed 26 November 2006
Citing this page:
Tilgner, Erich. 2006. Euphasmida. Stick & Leaf Insects. Version 26 November 2006. http://tolweb.org/Euphasmida/13636/2006.11.26 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/













 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site